- Ways to Find Out List of All Open Ports in Linux
- Method 1: Using netstat tool
- Method 2: Using ss tool
- Method 3: lsof command
- 4 Ways to Find Out What Ports Are Listening in Linux
- 1. Using Netstat Command
- 2. Using ss Command
- 3. Using Nmap Command
- 4. Using lsof Command
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- How to List Open Ports on Linux?
- Ports on Linux
- List Open Ports
- List protocols and open ports from /etc/services
- List open ports using netstat
- List open ports using ss
- List open ports using lsof
- List open ports using nmap
- List open ports using netcat
- Final Thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
Ways to Find Out List of All Open Ports in Linux
In this article, we are going to see how to find out the list of all open ports in linux. Ports are the endpoint of communication in the computer networks, or we can also say that the port is working as the door for communication on the computer network. The ports are basically 16-bit numbers (from 0 to 65535). These ports are used to communicate by the Internet transport protocols like the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
The ports are categorized by the range of port number as follows:
- From 0 to 1023: These ports are known as the Well-known ports. These ports can only be used by system (or root) processes or by programs executed by privileged users.
- From 1024 to 49151:These ports are known as the Registered ports. These ports can be used by ordinary user processes or programs executed by ordinary users.
- From 49152 to 65535:These ports are known as Dynamic Ports.
We are going to see what are the by which we can find out the list of open ports in the Linux systems. But before that to get the list of all port on the system, you can use the following command:
Now let’s see how to find out the list of open ports in the Linux systems.
There are three ways by which we can find the list of open ports on the Linux system. Let’s see them one by one.
Method 1: Using netstat tool
The netstat is a tool which give the information about the Linux networking subsystem. We use the netstat to list all open ports on the system. Use the following command to list all open ports on the system.
In the above command:
- Option -l: list only listening sockets.
- Option -n: show the port number.
- Option -t: list the TCP ports.
- Option -u: list the UDP ports
Method 2: Using ss tool
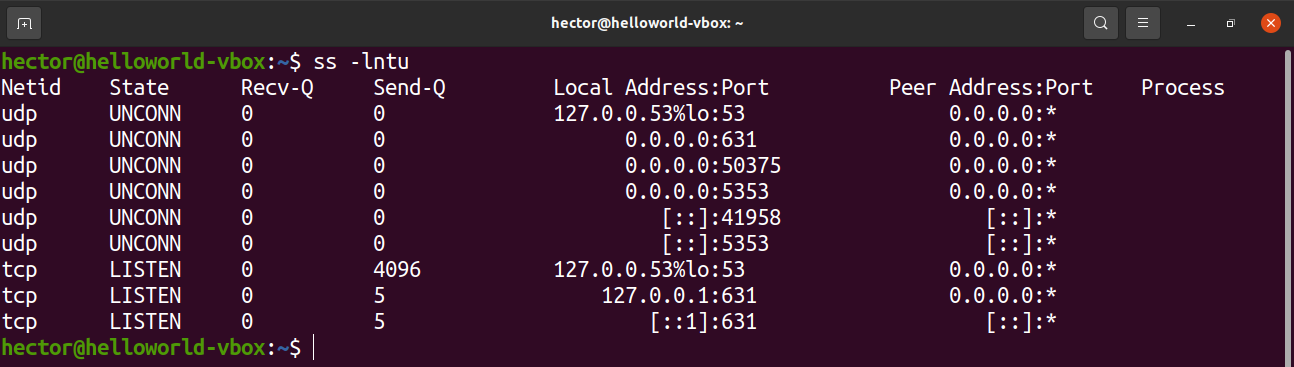
ss is another tool to investigate sockets. Which is the best alternative to the netstat command. So we can also use the ss tool to list the open ports on the system. Use the following command to list the all ports on the system.
The meaning of all options used with the above command are the same as the previous netstat command.
Method 3: lsof command
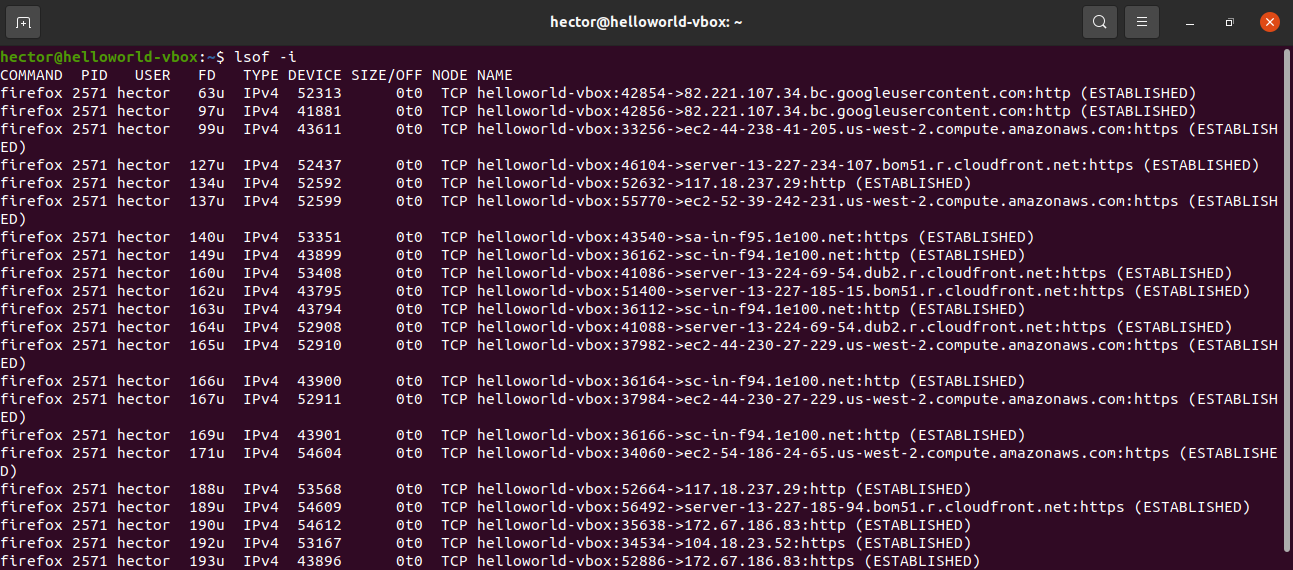
lsof is the command which is used to list the files. We can use the lsof command to list the open ports on the system using the following command:
In the above command:
- Option -i: selects the listing of files, any of whose Internet address matches the address specified in i.
- Option -P: inhibits the conversion of port numbers to port names for network files.
- Option -n: inhibits the conversion of network numbers to host names for network files
So we have learned how to leas the all open ports in the Linux system. To know more above the above command, read the man page of the above commands.
4 Ways to Find Out What Ports Are Listening in Linux
The state of a port is either open, filtered, closed, or unfiltered. A port is said to be open if an application on the target machine is listening for connections/packets on that port.
In this article, we will explain four ways to check open ports and also will show you how to find which application is listening on what port in Linux.
1. Using Netstat Command
Netstat is a widely used tool for querying information about the Linux networking subsystem. You can use it to print all open ports like this:
The flag -l tells netstat to print all listening sockets, -t shows all TCP connections, -u displays all UDP connections and -p enables printing of application/program name listening on the port.

To print numeric values rather than service names, add the -n flag.

You can also use grep command to find out which application is listening on a particular port, for example.

Alternatively, you can specify the port and find the application bound to, as shown.

2. Using ss Command
ss command is another useful tool for displaying information about sockets. It’s output looks similar to that of netstat. The following command will show all listening ports for TCP and UDP connections in numeric value.

3. Using Nmap Command
Nmap is a powerful and popular network exploration tool and port scanner. To install nmap on your system, use your default package manager as shown.
To scan all open/listening ports in your Linux system, run the following command (which should take a long time to complete).
4. Using lsof Command
The final tool we will cover for querying open ports is lsof command, which is used to list open files in Linux. Since everything is a file in Unix/Linux, an open file may be a stream or a network file.
To list all Internet and network files, use the -i option. Note that this command shows a mix of service names and numeric ports.

To find which application is listening on a particular port, run lsof in this form.

That’s all! In this article, we have explained four ways to check open ports in Linux. We also showed how to check which processes are bound upon particular ports. You can share your thoughts or ask any questions via the feedback form below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
How to List Open Ports on Linux?
In networking, a port is an interesting feature. It’s a way for network traffic to identify the destination app or service. Each process/service gets its unique port. A port will always be associated with the IP address of the host along with the protocol.
This is a favorite metaphor of mine to describe what a port is. Imagine a ship loaded with cargo, which will travel to a distant land. What information is needed to reach the destination properly? For the sake of simplicity, let’s say it needs the country (the IP address) and the port the ship will dock.
In this guide, check out how to list open ports on Linux.
Ports on Linux
Ports act as an endpoint of communication. It’s a 16-bit number (0 to 65535 in decimal). While the range is large, for ease of use, ports are categorized into three categories. Each category is labeled as the range of port value:
- 0 to 1023: These are the “Well-known” ports, also known as the “System” ports, which are reserved for system processes that offer a wide variety of network services. To bind with a “Well-known” port, a process must have superuser privilege.
- 1024 to 49151: These are the “Registered” ports, also known as the “User” ports, that are designated by IANA for specific services. Upon request, a process may have access to them. In the case of most systems, it doesn’t require any superuser privilege to use these ports.
- 49152 to 65535: These are the “Dynamic” ports, also known as the “Private” ports. These ports can’t be registered with IANA. These ports are open to using for private or customized services and may also be automatically allocated as ephemeral ports (short-lived ports used by IP).
In Linux, there are multiple ways of checking the open ports. By default, any port will remain closed unless an app is using it. If a port is open, then it must be assigned to a service/process.
List Open Ports
It’s easier to identify which ports are in use rather than which ports are open. That’s why the following section will feature methods to list all the ports that are currently in use. In Linux, there are multiple tools available for the task. Most of them come built-in in any Linux distro.
Learning which ports are currently open can be useful in various scenarios. It’s possible to configure a dedicated port for a certain application. An open port may also be a strong indication of intrusion in the network.
The following methods are demonstrated on Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS.
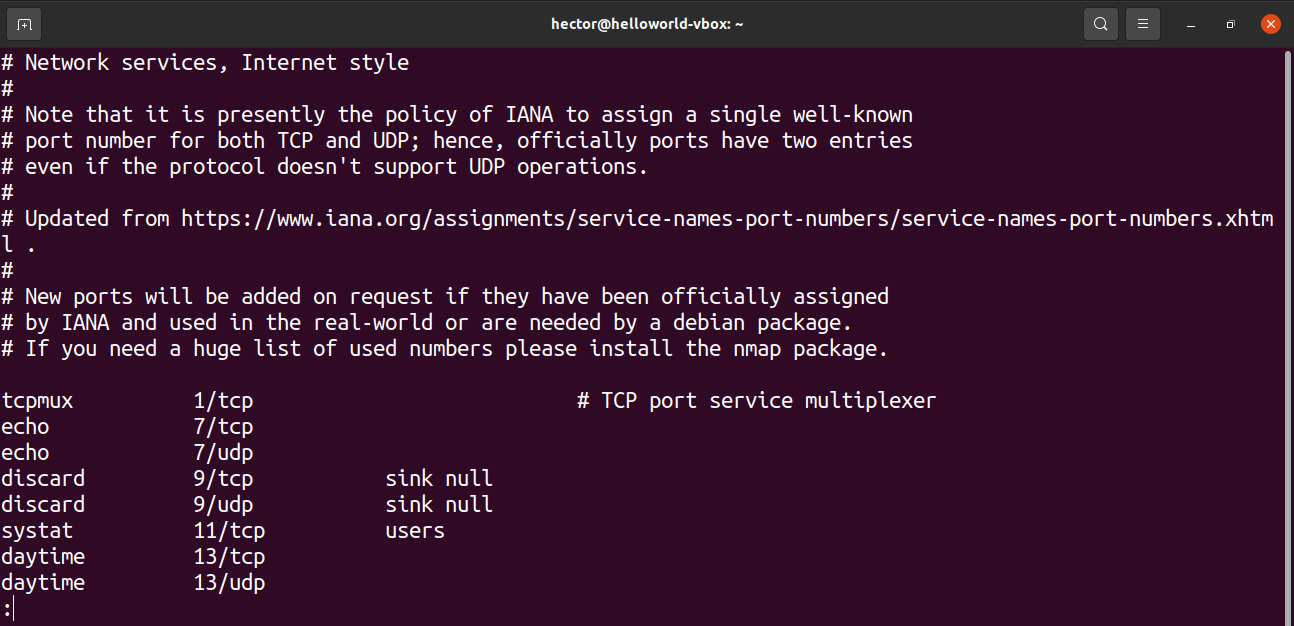
List protocols and open ports from /etc/services
The /etc/services file contains information about the currently running services. It’s a big file, so ready to get overwhelmed.
List open ports using netstat
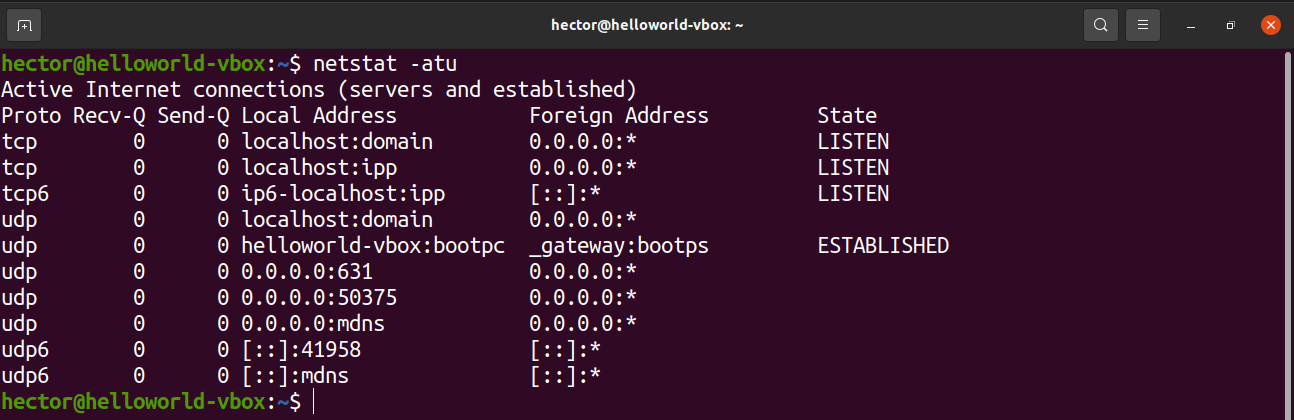
The netstat tool is a utility for displaying network connections for TCP, routing tables, and various network interfaces. It also offers network protocol statistics. By using netstat, we can list all the open ports of the system.
Run the following netstat command:
Let’s have a quick breakdown of all the flags we used in this command.
- a: Tells netstat to show all sockets
- t: Tells netstat to list TCP ports
- u: Tells netstat to list UDP ports
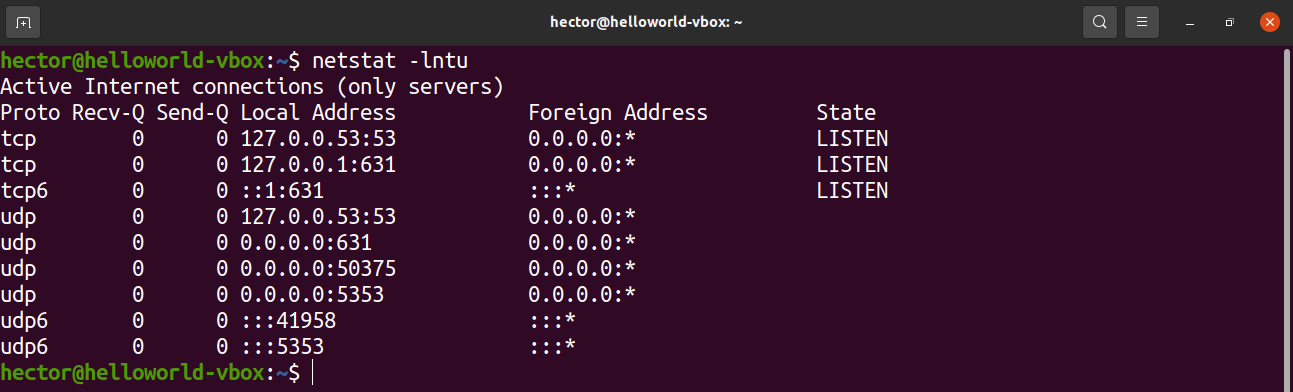
Here’s another variation of the netstat command:
There are two new flags used in the command. What do they mean?
- l: Tells netstat to print only the listening sockets
- n: Tells netstat to show the port number
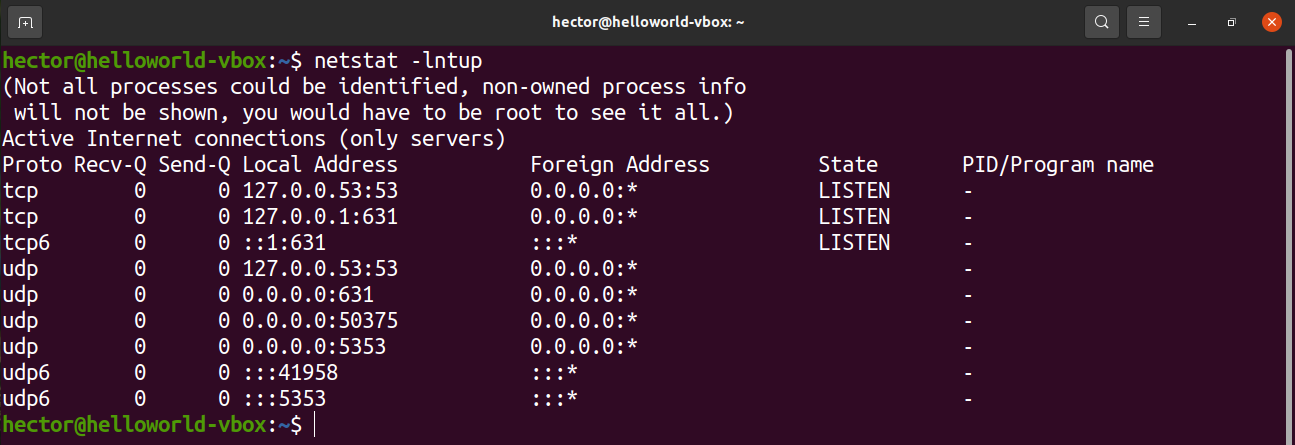
To display the PID of the process that’s using a port, use the “-p” flag:
List open ports using ss
The ss tool is a utility for investigating socket. Its usage is similar to netstat.
To list the open ports, run the following ss command:
The flags are similar to netstat. The functions they describe are also quite similar.
- l: Tells ss to display listening sockets
- n: Tells ss not to try to resolve service names
- t: Tells ss to display TCP sockets
- u: Tells ss to display UDP sockets
List open ports using lsof
The lsof command is to list open files. However, it can also be used for displaying the open ports.
Run the following lsof command:
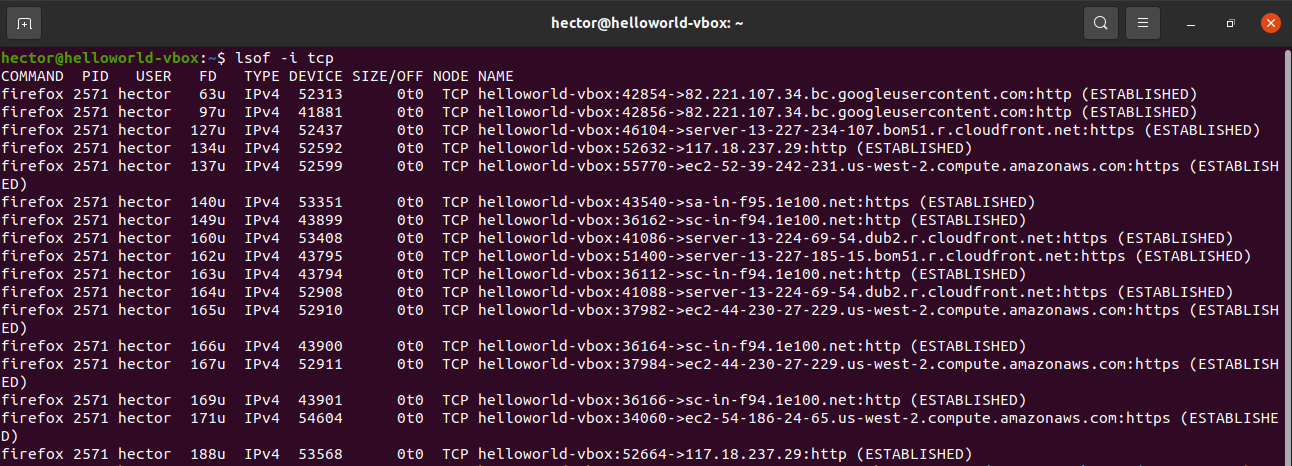
To get the open ports of a specific protocol (TCP, UDP, etc.) then define it after the “-i” flag, use:
List open ports using nmap
The nmap tool is a powerful one for network exploration and security/port scanning. It can report all the open ports in the system.
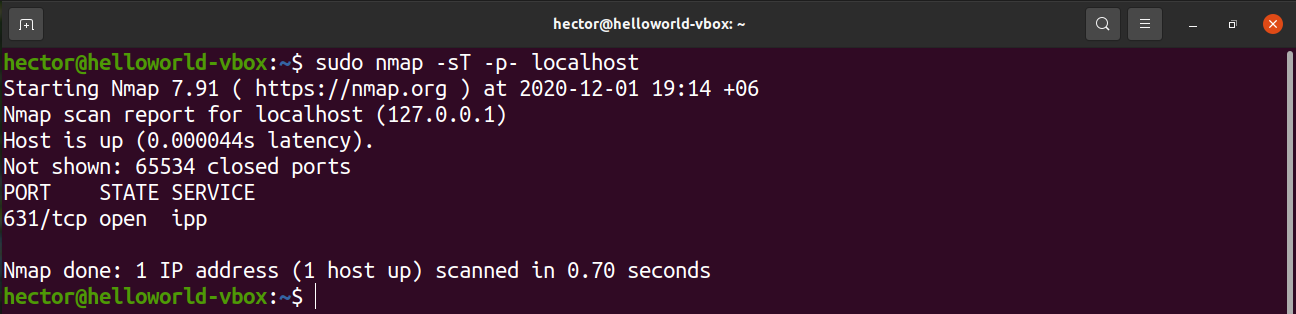
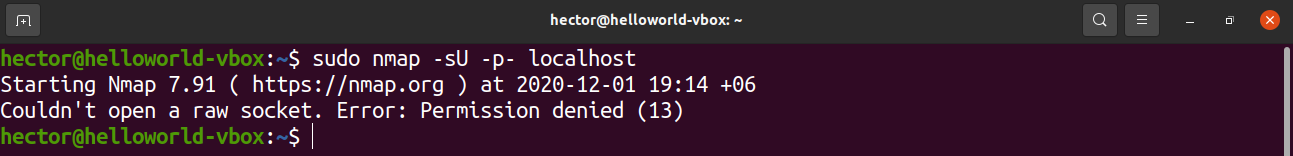
To list the open TCP ports, run the following nmap command. Here, the IP address is of the host computer:
Here, there are two portions of the command argument.
- -sT: This section tells nmap to scan for TCP ports.
- -p- : This tells nmap to scan for all 65535 ports. If not used, then nmap will scan only 1000 ports by default.
If you need to list the open UDP ports, then run the following nmap command:
To get both the open TCP and UDP ports, use the following command:
List open ports using netcat
The netcat tool is a command line utility for reading and writing data across network connections over the TCP and UDP protocols. This tool can also be used for listing open ports. It can perform tests on a specific port or a range of ports.
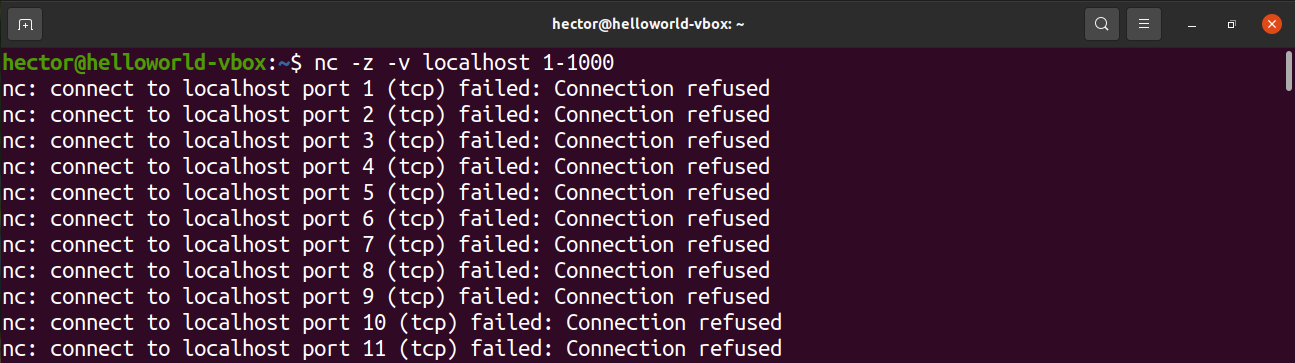
The following netcat command will scan the port from 1 to 1000. The netcat command will perform the scan on TCP protocol by default:
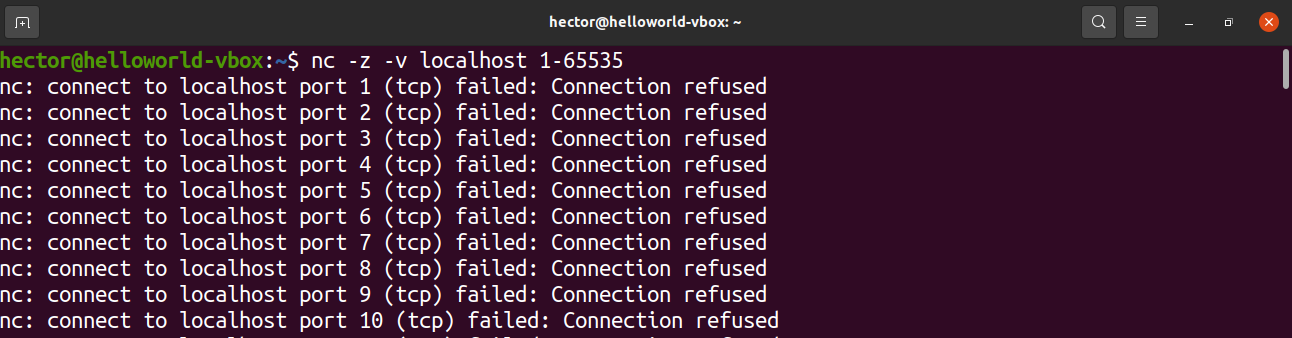
It can also be extended to the entire list of possible ports:
Let’s have a quick breakdown of the flags.
- z: Tells netcat to scan only for open ports without sending any data
- v: Tells netcat to run in verbose mode
To get only the open ports from this list, filter the output with grep for the term “succeeded”.
If you want to perform the scan on UDP protocol, then add the “-u” flag.
Final Thoughts
As demonstrated, there are tons of ways to scan for open ports on Linux. I suggest trying out all the methods before you decide which one to master. If you’re using a certain tool like netcat or nmap regularly, then mastering the associated methods will be the most beneficial.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.